If you've followed the steps to connect your Mac to a Wi-Fi network, but the connection to your network or the Internet isn't reliable, the steps in this article might help.
Check for Wi-Fi recommendations
WiFi Explorer detects 802.11a/b/g/n/ac wireless networks, works with 2.4 and 5GHz channel bands, and 20, 40, 80 and 160 MHz channels. This wifi analyzer tool can keep an eye on network signal strength consistently and provide you with metrics and network details that can be exported to a CSV file.
- This app helps you quickly and easily check your Wi-Fi network strength in your Menu Bar. You can also view your network name, your public IP address, your local IP address, and your MAC address from the Menu Bar. The percentage in the toolbar icon represents the strength of your connection between your router and your computer.
- Jul 06, 2019 If you still have issues, the network is the problem. If the ethernet connection is fine and a router reset didn’t help, then it’s time to check signal strength. Checking Wi-Fi Signal Strength the Easy Way. To check the strength of your Wi-Fi, the first thing to do is look at the device having issues.
When your Mac tries to connect to a Wi-Fi network, it checks for issues that affect its ability to create a fast, stable, and secure connection. If an issue is detected, the Wi-Fi status menu in the menu bar shows a new item: Wi-Fi Recommendations. Choose it to see recommended solutions.
Wi-Fi recommendations are available in macOS Sierra or later.
Analyze your wireless environment
Your Mac can use Wireless Diagnostics to perform additional analysis.
- Quit any apps that are open, and connect to your Wi-Fi network, if possible.
- Press and hold Option (Alt) ⌥ key, then choose Open Wireless Diagnostics from the Wi-Fi status menu .
- Enter your administrator name and password when prompted.
Wireless Diagnostics begins analyzing your wireless environment:
If the issue is intermittent, you can choose to monitor your Wi-Fi connection:
When you're ready to see recommendations, continue to the summary. Wireless Diagnostics asks for optional information about your base station or other router, so that it can include that in the report it saves to your Mac.
Click the info button next to each item in the summary to see details about that item. Wi-Fi best practices are tips that apply to most Wi-Fi networks.
Back up or make note of your network or router settings before changing them based on these recommendations—in case you need to use those settings again.
Monitor your Wi-Fi connection
Your Mac can monitor your Wi-Fi connection for intermittent issues, such as dropped connections. Follow the steps to analyze your wireless environment, but choose ”Monitor my Wi-Fi connection” when prompted.
During monitoring, a window shows that monitoring is in progress. Monitoring continues as long as this window is open and you're on the same Wi-Fi network, even when your Mac is asleep.
If Wireless Diagnostics finds an issue, it stops monitoring and shows a brief description of the issue. You can then resume monitoring or continue to the summary for details and recommendations.
Create a diagnostics report
Wireless Diagnostics automatically saves a diagnostics report before it displays its summary. You can create the same report at any time: press and hold the Option key, then choose Create Diagnostics Report from the Wi-Fi status menu . It can take your Mac several minutes to create the report.
- macOS Sierra and later saves the report to the /var/tmp folder of your startup drive, then opens that folder for you.
To open the folder manually, choose Go > Go to Folder from the Finder menu bar, then enter /var/tmp. - OS X El Capitan or earlier saves the report to your desktop.
The report is a compressed file with a name that begins “WirelessDiagnostics.” It contains many files that describe your wireless environment in detail. A network specialist can examine them for further analysis.
Use other diagnostics utilities
Wireless Diagnostics includes additional utilities for network specialists. Open them from the Window menu in the Wireless Diagnostics menu bar:
- Info gathers key details about your current network connections.
- Logs enables background logging for Wi-Fi and other system components. The result is saved to a .log file in the diagnostics report location on your Mac. Logging continues even when you quit the app or restart your Mac, so remember to disable logging when you're done.
- Scan finds Wi-Fi routers in your environment and gathers key details about them.
- Performance uses live graphs to show the performance of your Wi-Fi connection:
- Rate shows the transmit rate over time in megabits per second.
- Quality shows the signal-to-noise ratio over time. When the quality is too low, your device disconnects from the Wi-Fi router. Factors that affect quality include the distance between your device and the router, and objects such as walls that impede the signal from your router. Learn more.
- Signal shows both signal (RSSI) and noise measurements over time. You want RSSI to be high and noise to be low, so the bigger the gap between RSSI and noise, the better.
- Sniffer captures traffic on your Wi-Fi connection, which can be useful when diagnosing a reproducible issue. Select a channel and width, then click Start to begin capturing traffic on that channel. When you click Stop, a .wcap file is saved to the diagnostics report location on your Mac.
Learn more
Additional recommendations for best Wi-Fi performance:
- Keep your router up to date. For AirPort Time Capsule, AirPort Extreme, or AirPort Express Base Station, check for the latest firmware using AirPort Utility. For non-Apple routers, check the manufacturer's website.
- Set up your router using Apple's recommended settings, and make sure that all Wi–Fi routers on the same network use similar settings. If you're using a dual-band Wi-Fi router, make sure that both bands use the same network name.
- Learn about potential sources of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth interference.
Learn about other ways to connect to the Internet.
Today, one can only imagine what they would do without the internet and WiFi. While wired connections are still pretty much prevalent, nothing really beats the convenience of WiFi and wireless networks are also catching up in terms of speed. In this article, we are going to talk about how you can get the most out of your WiFi network by monitoring the performance of your network and improving it with these Wi-Fi analyzing tools for macOS.
Note: Most of these apps only work with the built-in WiFi adapter of your Mac and do not work with an external adapter.
Also Read: 10 Best WiFi Analyzer for Windows 10/8/7
1. macOS WiFi Analyser
macOS itself comes with a Wireless Diagnostics tool which you can use to scan all available wireless networks and get a summary of all the channels that your device can connect to. From the summary, it is able to suggest the best 2.4 GHz or 5GHz channel or network suitable for you. It can also be used to monitor the network performance, get log information and even as a sniffer to capture WiFi traffic.
To access it, while holding the Option key click on the WiFi icon in the menu bar and you should see an option as “Open Wireless Diagnostics” which should take you to your built-in WiFi analyzer. Or simply you can also open Spotlight Search and type in “Wireless Diagnostics”.
Pros:
Mac Network Settings
- Network Scanner
- Monitor performance of connected WiFi
- Log Info
- Channel Suggestions
Cons:
- Non-intuitive UI
- No graphical representations
Verdict:
You can get away with the Wireless Diagnostics tool if you need to troubleshoot some minor issues in your personal network. Although it is not very powerful, given it comes built-in and free, you can’t really complain.
2. WiFi Signal
WiFi Signal is one of the more simpler apps on this list which provides all the information you need about your wireless network in a compact and elegant card fashion. The app lives on your menu bar, the icon of which can be fully customized and clicking on it gives you everything from the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) to the max data rate and MCS index of your connection. There is a real-time graphical representation of the signal rate and noise rate and the app can also recommend the best channel.
Read: Create a WiFi hotspot from Android which is already connected to WiFi
Pros:
- Customizable menubar icon with live signal rate
- Simple at a glance information
- Notifications support
- Channel recommendations
Cons:
- Info of only connected network
- No WiFi scanner
Verdict:
If you are someone who needs to check the strength or quality of your current network from time to time, this app provides you all the info in an elegant card fashion along with a customizable menu bar icon.
Download WiFi Signal ($4.99)
3. WiFi Explorer
WiFi Explorer is one of the highest rated WiFi analyzer apps on the Mac App Store and rightfully so. The app does a great job at scanning, monitoring, and troubleshooting wireless networks.
The app provides various real-time graphs for network details, signal strength, and spectrum which makes it much more intuitive for even a normal person to effectively use the app. Apart from the details of your connected network, the graphs also display all the networks your device can connect to, along with all their details which comes in really handy for choosing the strongest access point for your computer. A bonus feature of this app is that you can save all the results for a later review and even export all the network details as a CSV file.
Pros:
- Graphical visualizations of the WiFi environment
- Detailed descriptions of access points
- Exportable to CSV format
Cons:
- Pricey for the number of features it offers
- No menubar icon
Verdict:
Network Strength For Mac Os
Wi-Fi Explorer is great for quickly identifying channel conflicts, signal overlapping or configuration problems that may be affecting the connectivity and performance of your home, office or enterprise wireless network.
Download WiFi Explorer ($19.99)
4. Wifi Scanner
The next app on our list is WiFi Scanner which adds a number of nifty features to the standard WiFi analysis tool.
Like the previous apps, it comes with various real-time and color co-ordinated graphs of the various available networks and provides details about them. But it doesn’t stop there as WiFi Scanner also brings a built-in WiFi speed testing feature that showcases the ping, download and upload speeds of your network to troubleshoot WiFi networks. There is also an extremely useful IP Scanner feature which will give you a list of all the devices that are connected to your network which is great for finding those WiFi “piggybackers”.
Pros:
- Real time graphs and detailed network parameters
- Speed Testing tool
- IP Scanner
- Exportable to CSV format
Cons:
- No menubar icon or way to quickly glance at any info without opening up the app
Verdict:
Personally to me, WiFi Scanner seems the most bang for your buck and with all its features it functions like an all-in-one from scanning available networks and their performances to seeing which devices are connected to my network.
Download WiFi Scanner ($19.99)
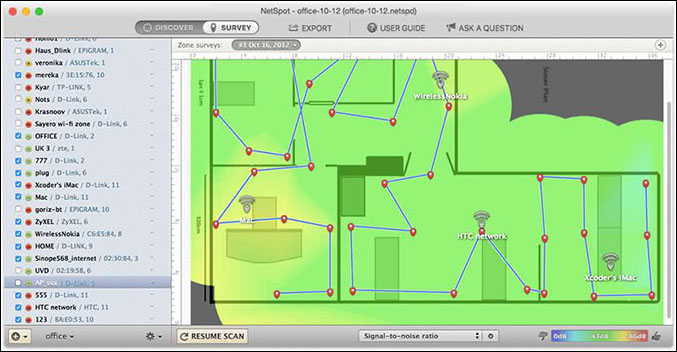
5. NetSpot
NetSpot offers the convenient visual heat maps so you can easily catch any dead spots and how you can optimize access points locations; it is a WiFi analyzer tool like no other!
The app allows you to directly upload a map of your area or draw one using NetSpot’s map drawing tool. Once you have completed that, you can select between several visualizations like signal level, noise level, and access points which show you everything throughout the whole map in the form of heat maps. You can then identify the areas with low signal strength or problems and troubleshoot them.
Pros:
- Full Network analysis and surveys
- Support for area plan or map
- Heat map visualizations
- Suitable for commercial use
Cons:
- Very pricey for personal use
Verdict:
NetSpot feels like a well polished complete WiFi analyzer app. It does feel a little redundant for personal use but with its commercial licensing, it should work great for commercial use or large office areas to detect dead zones and improve the overall connectivity of the area.
Download NetSpot (Freemium)
6. Honorable Mentions
WireShark is an open source and very powerful network analyzer used mainly by network admins and developers. Although it comes with a steep learning curve, it is one of the best packet analyzer apps available. WireShark is also capable of working in monitor mode, thereby letting you see what other devices are browsing/watching on your network. While normally you’d need an external WiFi adapter to these kinds of things, most Macs have a network card that supports monitor mode which overall works out pretty well.
JamWiFi is another free little tool which can not only analyze devices connected to your wireless network, but you can also disconnect them from using your WiFi. But it also comes with a downside which is it will also disconnect you and you have to reconnect again.

WiFi Signal Strength Explorer is a handy little utility which unlike the normal WiFi icon, shows you the strength of connection via dots/percent in the menu bar and by clicking it, you can access some basic details about your current network.
Wrapping Up: WiFi Analyser for Mac
So these were the best WiFi analyzer applications available for macOS and here’s a little recap. For casual use or not too deep analysis, the Wireless Diagnostics seem to work just fine. If you need something quick that shows you details about your connected network just from your menubar, check out WiFi Signal. As a WiFi analyzing tool, WiFi Explorer has got everything you might need. However, if you are a sucker for extra features, WiFi Scanner provides the most for your money. For large organizations or commercial purposes, nothing comes close to NetSpot. Did we miss anything? Which one do you use? Let us know in the comments below.
Network Strength For Mac Catalina
Read: 10 Step by Step Fix to WiFi Connected But No Internet Access
